Does The Hardness Of Silicone Change As The Viscosity Changes
Silicone safety is an elastomer (rubber-like material) composed of silicone—itself a polymer—containing silicon together with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Silicone rubbers are widely used in industry, and there are multiple formulations. Silicone rubbers are oftentimes 1- or two-part polymers, and may incorporate fillers to improve backdrop or reduce price. Silicone condom is mostly non-reactive, stable, and resistant to extreme environments and temperatures from −55 to 300 °C (−70 to 570 °F) while still maintaining its useful properties. Due to these properties and its ease of manufacturing and shaping, silicone rubber can be found in a wide multifariousness of products, including voltage line insulators; automotive applications; cooking, baking, and food storage products; apparel such as undergarments, sportswear, and footwear; electronics; medical devices and implants; and in home repair and hardware, in products such as silicone sealants.
Curing [edit]
In its uncured state, silicone rubber is a highly agglutinative gel or liquid. To convert information technology to a solid, it must be cured, vulcanized, or catalyzed. This is ordinarily carried out in a ii-phase process at the bespeak of industry into the desired shape, and then in a prolonged post-cure process. It can besides exist injection molded.
Silicone prophylactic may be cured by a platinum-catalyzed cure system, a condensation cure system, a peroxide cure system, or an oxime cure system. For the platinum-catalyzed cure system, the curing process can exist accelerated past adding heat or pressure level.
Platinum-based cure system [edit]
In a platinum-based silicone cure arrangement, also called an improver organisation (because the cardinal reaction-building polymer is an improver reaction), a hydride- and a vinyl-functional siloxane polymer react in the presence of a platinum complex catalyst, creating an ethyl bridge between the 2.[1] The reaction has no byproducts. Such silicone rubbers cure apace, though the rate of or even ability to cure is hands inhibited in the presence of elemental can, sulfur, and many amine compounds.[2]
Condensation cure arrangement [edit]
Condensation curing systems tin be 1-part or two-part systems.[3] In one-part or RTV (room-temperature vulcanizing) system, a cross-linker exposed to ambience humidity (i.east., water) experiences a hydrolysis step and is left with a hydroxyl or silanol group. The silanol condenses further with some other hydrolyzable group on the polymer or cross-linker and continues until the organisation is fully cured. Such a system will cure on its own at room temperature and (unlike the platinum-based addition cure system) is non easily inhibited past contact with other chemicals, though the process may be affected by contact with some plastics or metals and may not take identify at all if placed in contact with already-cured silicone compounds. The crosslinkers used in condensation cure systems are typically alkoxy, acetoxy, ester, enoxy or oxime silanes such as methyl trimethoxy silane for alkoxy-curing systems and methyl triacetoxysilane for acetoxy-curing systems. In many cases an additional condensation catalyst is added to fully cure the RTV organization and achieve a tack-free surface. Organotitanate catalysts such as tetraalkoxy titanates or chelated titanates are used in alkoxy-cured systems. Can catalysts such as dibutyl tin dilaurate (DBTDL) tin be used in oxime and acetoxy-cured systems. Acetoxy tin condensation is one of the oldest cure chemistries used for curing silicone rubber, and is the ane used in household bathroom caulk. Depending on the type of detached molecule, it is possible to allocate silicone systems equally acidic, neutral or alkaline.[4]
![]()
Overview of the most commonly used silicone systems
2-part condensation systems parcel the cross-linker and condensation catalyst together in one role while the polymer and any fillers or pigments are in the 2nd part. Mixing of the two parts causes the curing to have place. A typical filler is fumed silica, besides known as pyrogenic silica, which used to control the flow backdrop of the sealant. [five]
Once fully cured, condensation systems are effective as sealants and caulks in plumbing and edifice structure and as molds for casting polyurethane, epoxy and polyester resins, waxes, gypsum, and low-melting-temperature metals such every bit pb. They are typically very flexible and have a high tear strength. They exercise not crave the use of a release agent since silicones have non-stick properties.
Peroxide cure system [edit]
Peroxide curing is widely used for curing silicone rubber. The curing process leaves backside byproducts, which can be an event in food contact and medical applications. However, these products are usually treated in a postcure oven which greatly reduces the peroxide breakdown product content. 1 of the ii main organic peroxides used, dicumyl peroxide (compare cumene hydroperoxide), has principal breakdown products of acetophenone and phenyl-2-propanol. The other is dichlorobenzoyl peroxide, whose primary breakdown products are dichlorobenzoic acid and dichlorobenzene.[half dozen]
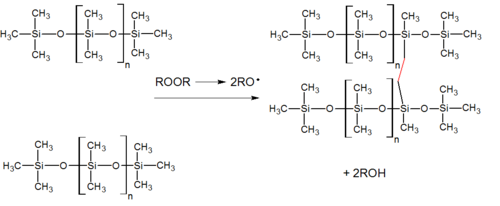
Crosslinking by organic peroxides
History [edit]
The first silicone elastomers were developed in the search for improve insulating materials for electric motors and generators. Resin-impregnated glass fibers were the state-of-the-art materials at the fourth dimension. The drinking glass was very heat resistant, but the phenolic resins would not withstand the higher temperatures that were being encountered in new smaller electric motors. Chemists at Corning Glass and General Electric were investigating oestrus-resistant materials for use as resinous binders when they synthesized the offset silicone polymers, demonstrated that they worked well and found a route to produce them commercially.
The term "silicone" is actually a misnomer. The suffix -one is used by chemists to announce a substance with a double-bonded atom of oxygen in its backbone. When first discovered, silicone was erroneously believed to have oxygen atoms bonded in this mode. Technically correct term for the diverse silicone rubbers is polysiloxanes or polydimethylsiloxanes.[2]
Corning Glass in a joint venture with Dow Chemic formed Dow Corning in 1943 to produce this new class of materials. As the unique properties of the new silicone products were studied in more particular, their potential for broader usage was envisioned, and GE opened its own institute to produce silicones in 1947. GE Silicones was sold to Momentive Performance Materials in 2006.[7] Wacker Chemie as well started production of silicones in Europe in 1947. The Japanese visitor Shin-Etsu Chemic began mass production of silicone in 1953.
Properties [edit]
Silicone rubber offers good resistance to extreme temperatures, being able to operate ordinarily from −100 to 300 °C (−150 to 570 °F). Silicone rubber has low tensile strength, poor clothing and tear wear backdrop.[8] Some backdrop such as elongation, pitter-patter, cyclic flexing, tear forcefulness, compression prepare, dielectric strength (at high voltage), thermal conductivity, burn resistance and in some cases tensile strength tin be—at extreme temperatures—far superior to organic rubbers in general, although a few of these backdrop are all the same lower than for some specialty materials. Silicone safe is a material of pick in manufacture when retention of initial shape and mechanical strength are desired under heavy thermal stress or sub-naught temperatures.[ix] [ten] [xi]
Compared to organic safety [edit]
Organic safe has a carbon-to-carbon courage which tin leave it susceptible to ozone, UV, estrus and other aging factors that silicone rubber can withstand well. This makes silicone rubber 1 of the elastomers of pick in many farthermost environments. Silicone is considerably more than permeable to gasses than about other rubbers which limits its utilize in some areas.
Silicone safety is highly inert and does non react with near chemicals and isn't available to participate in biological processes assuasive it to exist used in many medical applications including medical implants. It is biocompatible, hypoallergenic, which makes it suitable for infant care products, and food contact in general. Silicone condom is a reliable solution (every bit opposed to rubber and thermoplastic elastomers) for migration or interaction bug between the main agile ingredients. Its chemic stability prevents it from affecting any substrate information technology is in contact with (skin, water, blood, active ingredients, etc.).[12]
-
Property Value Appearance Hardness, Shore A 25–xc Tensile failure stress, ultimate ane,400–10,300 kPa (200–1,500 psi) Elongation after fracture in % ≥ 700% maximum Density Tin can exist compounded from 0.95 to over one.twenty g/cmthree
Production [edit]
To make silicone, the silicon atoms must be isolated from the silicon dioxide compound silica. This is done by heating large volumes of quartz sand to extremely high temperatures, frequently up to 1800 °C. From here, in that location are several processes where silicon is combined with methyl chloride and heated. Information technology is and so distilled into a polymerised siloxane known equally polydimethylsiloxane. The polydimethylsiloxane tin then be polymerised. This is done using a variety of techniques depending on the use of the final product.[13] The raw silicone compound is combined with whatever desired additives, which may include pigments, and the catalyst. It is then injection moulded or extruded. Curing is the final phase in the production process.
Structure [edit]
![]()
Polysiloxanes differ from other polymers in that their backbones consist of Si–O–Si units dissimilar many other polymers that incorporate carbon backbones. Polysiloxane is very flexible due to big bond angles and bail lengths when compared to those found in more than basic polymers such equally polyethylene. For example, a C–C backbone unit has a bail length of one.54 Å and a bond bending of 112°, whereas the siloxane backbone unit Si–O has a bond length of 1.63 Å and a bail angle of 130°.
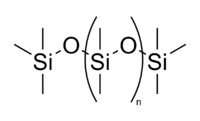
The siloxane backbone is a more than flexible polymer than the bones carbon chain backbone because the side groups are spaced farther apart. Polymer segments can move farther and modify conformation easily, making for a flexible material. Polysiloxanes tend to be more stable and less chemically agile because more energy is required to break the silicon-oxygen bond. Although silicon is a congener of carbon, having the aforementioned electron bonding configuration, silicon analogues of carbonaceous compounds mostly exhibit dissimilar properties. The difference in total charge and mass betwixt carbon with 6 protons and half dozen neutrons, and silicon with xiv protons and fourteen neutrons causes an added layer of electrons and their screening effect changes the electronegativity betwixt the two elements. For example the silicon-oxygen bond in polysiloxanes is significantly more than stable than the carbon-oxygen bond in polyoxymethylene, a structurally similar polymer. The divergence is partly due to the higher bond free energy, the free energy required to pause the Si-O bond, and also because polyoxymethylene decomposes formaldehyde, which is volatile and escapes driving decomposition forward, merely Si-containing decomposition products of silicone are less volatile and [fourteen].[15]
-
Mechanical properties (Polymax 2005)[ citation needed ] Hardness, shore A 10–90 Tensile strength 11 N/mm2 Elongation at break 100–1100 % Maximum temperature 300 °C Minimum temperature −120 °C
Special grades [edit]
In that location are many special grades and forms of silicone condom, including: steam resistant, metallic detectable, high tear forcefulness, extreme loftier temperature, farthermost low temperature, electrically conductive, chemic/oil/acid/gas resistant, low fume emitting, and flame-retardant. A multifariousness of fillers can exist used in silicone safe, although most are non-reinforcing and lower the tensile strength.
Silicone rubber is bachelor in a range of hardness levels, expressed as Shore A or IRHD between 10 and 100, the higher number being the harder chemical compound. Information technology is too bachelor in nearly any colour, and tin can be colour matched.
![]()
Applications [edit]
![]()
A silicone safe pastry brush.
Once mixed and coloured, silicone rubber tin be extruded into tubes, strips, solid cord or custom profiles according to the size specifications of the manufacturer. Cord can be joined to brand O-rings and extruded profiles tin can exist joined to make seals. Silicone rubber can exist moulded into custom shapes and designs. Manufacturers work to set industry tolerances when extruding, cut or joining silicone safe profiles. In the Britain this is BS 3734, for extrusions the tightest level is E1 and the widest is E3.
Silicone rubber is used in automotive applications, many cooking, baking, and food storage products, apparel including undergarments, sportswear, and footwear, electronics, to dwelling house repair and hardware, and a host of unseen applications.
Liquid silicone rubber is too manufactured for life science applications (syringe pistons, closure for dispensing arrangement, gaskets for Iv flow regulator, respiratory masks, implantable chambers for IV administration), cosmetic products (Mascara brush, make-upwardly packaging, make-upward applicator and lipstick moulds) and eyes products (circular lens, collimators, Fresnel lenses and complimentary grade lenses).[16]
Freeze-tolerant solar water-heating panels exploit the elasticity of silicone to repeatedly accommodate the expansion of water on freezing, while its extreme temperature tolerance maintain a lack of brittleness beneath freezing and excellent tolerance of temperatures in excess of 150 °C (300 °F). Its belongings of not having a carbon backbone, merely a chemically robust silicon backbone instead, reduces its potential as a food source for dangerous waterborne bacteria such every bit Legionella.
Non-dyed silicone rubber record with an fe(III) oxide additive (making the tape a ruby-red-orange colour) is used extensively in aviation and aerospace wiring applications as a splice or wrapping tape due to its non-flammable nature. The iron oxide additive adds loftier thermal conductivity but does non change the high electric insulation property of the silicone rubber. This type of self-amalgamating record amalgamates or fuses to itself, and then that when stretched and wrapped effectually cables, electrical joints, hoses and pipes information technology bonds into a strong seamless rubbery electrically insulating and waterproof layer, although not adhesive. As an electrical insulator, silicone rubber has the added virtue of remaining non-conductive when damaged by oestrus, reducing the likelihood of runaway arcing.
With the addition of carbon or another conductive substance as a powdered filler, silicone rubber can be made electrically conductive while retaining about of its other mechanical properties. As such information technology is used for flexible contacts which close on being pressed, used in many devices such as computer keyboards and remote command handsets.
Self-healing [edit]
In 2007, silicone rubber formed the matrix of the first autonomic cocky-healing elastomer.[17] The microcapsule-based fabric was capable of recovering virtually all of the original tear strength. Additionally, this material had improved fatigue properties as evaluated using a torsion-fatigue test.[18]
Encounter also [edit]
- Injection molding of liquid silicone rubber
- Forensic engineering
- Forensic polymer engineering science
- Medical grade silicone
- RTV silicone
References [edit]
- ^ Mazurek, P.; Vudayagiri, S.; Skov, A. 50. How to Tailor Flexible Silicone Elastomers with Mechanical Integrity : A Tutorial Review. Chem Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1448–1464. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2019/cs/c8cs00963e#!divAbstract
- ^ a b Roux, Marie Ange (2007). "Processing pharmaceutical polymers". Pharmaceutical Polymers 2007. Smithers Rapra. p. 28. ISBN9781847350176.
- ^ Mittal, K. L and Pizzi, A. (Eds.), (2009), Handbook of Sealant Technology, CRC Press, p. 328-332. ISBN 9781420008630.
- ^ Manfred Pröbster, Industrial Sealants - Fundamentals, choice and applications, Verlag Moderne Industrie 2004
- ^ Page 12 https://world wide web.wacker.com/h/medias/6415-EN.pdf
- ^ M. J. Forrest, Nutrient Contact Rubbers ii - Products, Migration and Regulation, Rapra Review Reports, vol. 16, No. 2, Smithers Rapra Publishing, 2006 ISBN 1859575226.
- ^ "About GE Silicones". www.siliconeforbuilding.com . Retrieved 2020-06-23 .
- ^ Seal & Pattern Inc. | SILICONE (VMQ) O-RINGS & SILICONE GASKETS
- ^ "Feature Properties of Silicone Prophylactic Compounds" past Shin-Etsu Co. http://world wide web.silicone.jp/e/itemize/pdf/rubber_e.pdf
- ^ Overview of silicone rubber materials http://www.thefreelibrary.com/An+overview+of+silicone+rubber.-a0105557239
- ^ Silicone rubber backdrop http://www.timcorubber.com/rubber-materials/silicone.htm Archived 2016-12-fourteen at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "LSR Specific Properties".
- ^ "News - What is Silicone Made of? | Viking Extrusions". www.vikingextrusions.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2019-08-13. Retrieved 2019-08-13 .
- ^ "mica sheet". Retrieved 2021-08-25 .
- ^ "Feature properties of Silicone Rubber Compounds-'" (PDF). Shin-Etsu Silicone. Japan: Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. August 2016.
- ^ "CVA SILICONE | Liquid Silicone Rubber LSR | Your Manufacture".
- ^ Keller et al., A Self-Healing Poly(dimethyl siloxane) Elastomer, Advanced Functional Materials, v. 17, p. 2399–2404 (2007).
- ^ Keller et al., Torsion Fatigue Response of Self-Healing Poly(dimethyl siloxane) Elastomers, Polymer, v.49 p. 3136–3145 (2008).
Farther reading [edit]
- Brydson, John (1999) Plastics Materials, Butterworth, 9th Ed
- Lewis, PR, Reynolds, K and Gagg, C (2004) Forensic Materials Technology: Instance Studies, CRC Printing
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silicone_rubber
Posted by: bellgunfoop.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Does The Hardness Of Silicone Change As The Viscosity Changes"
Post a Comment